You might be building an application or website in the Cloud.
Before you go into production, you'll want to find out how well it's performing and how much load your infrastructure can handle.
We don't want to have any surprises once we "go live" and find out during production that the infra is not responsive enough.
Therefore a good piece of advice is to stress or load test your workload in order to find bugs or any bottlenecks within the application or infrastructure.
In this blog post, you'll be shown how to deploy the distributed load test on AWS solution and create and run your first load test on a target endpoint.
After that, you'll see what the results of the load test look like and how you can analyse the report.
How to set up a distributed load test with JMeter on AWS
Generally, you'll want to load or stress test your workload in AWS to find out the following things:
- Are the scaling policies configured correctly (scale-in/out cooldown)
- Are the specs of the ECS containers or EC2 instances provisioned in an optimized way (mem/CPU)?
- How does the database / caching layer behave?
- How does our setup compare to on-prem when we compare response times?
From the (application) side we want to know the following:
- What are the response times of the application when it's getting load tested under stress?
- Find out where possible bottlenecks are e.g. queries that take long
- Check the failure rate of the application e.g. HTTP response 5xx error codes.
1. Deploy the distributed load test template
AWS provides a complete load-testing solution from the AWS Solutions Library.
This contains an AWS CloudFormation template that deploys the following architecture.

It consists of two parts; a frontend with the dashboard for displaying the load-testing results and a backend containing an ECS Fargate cluster that runs the load-testing mechanism using Apache JMeter.
To launch the CloudFormation stack in the AWS Console, do the following:
- Go to the CloudFormation service in the AWS Region of choice.
- Create a new stack and use this specific template from the AWS Solutions Library.
- On the Create stack page, verify that the correct template URL shows in the Amazon S3 URL text box and choose Next.
- On the Specify stack details page, assign a name to your solution stack.
- Before deploying the template make sure to review the default parameters and change them to your own preferred values. The following table contains the available parameters including the default values of this stack.
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Admin Name | (requires input) | The user name for the initial solution administrator |
| Admin Email | (requires input) | Email address of the administrator user. After launch, an email will be sent to this address with console login instructions. |
| AWS Fargate VPC CIDR Block | 192.168.0.0/16 | CIDR block for the solution created Amazon VPC that will contain AWS Fargate. |
| AWS Fargate Subnet A CIDR Block | 192.168.0.0/20 | CIDR block for VPC subnet A. |
| AWS Fargate Subnet B CIDR Block | 192.168.16.0/20 | CIDR block for VPC subnet B. |
| AWS Fargate Security Group CIDR Block | 0.0.0.0/0 | CIDR block that restricts Amazon ECS container outbound access. |
| Docker Hub Credentials Secret | (optional input) | If you have a Docker Hub account and want to use it with this solution, enter the name of your Secrets Manager secret containing your Docker Hub credentials. |
Distributed load testing on AWS template parameter options
2. log in to the distributed load testing dashboard
Once the stack has been created, which takes approximately 15 minutes.
You then receive an email that contains the username, temporary password, and link to the distributed load testing dashboard.
3. Create and start a load test
Once you're logged in using the credentials and the URL, you'll see the dashboard with the past load tests that have been run.

At the top left of the dashboard, you see "Create test" to configure and start your first load test.
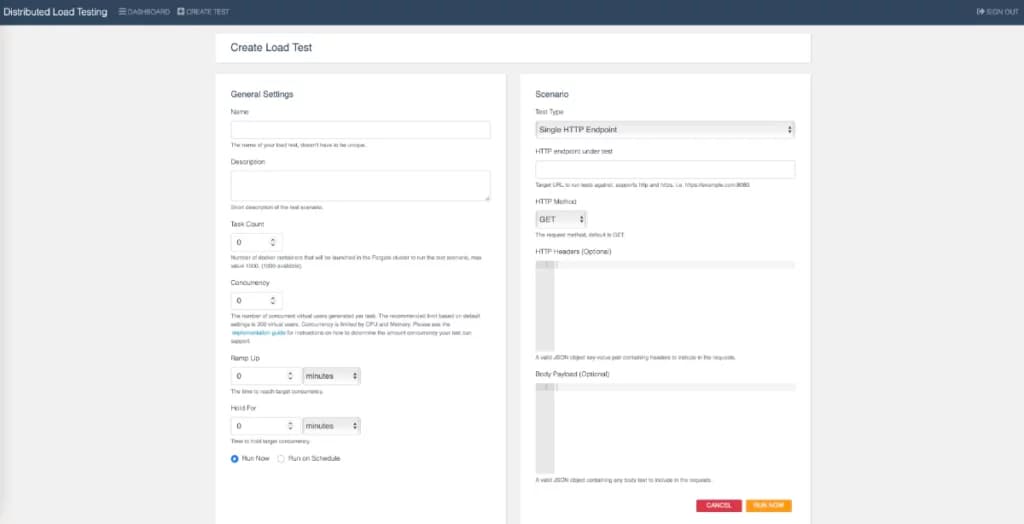
Here you insert the information for the load test to be able to start testing your workload.
Let's go over each individual setting and explain what it does:
| Action | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Name | Insert the name of the load test + (optional target name) |
| Description | Provide details of the target workload that you're load testing against. For example, I write down the specs of the container cluster that is running the application on which I do the distributed load test: ContainerCpu: 512 ContainerMemory: 1024 MinContainers: 2 MaxContainers: 50 AutoScalingCPU: - AutoScalingTargetValueCPU: 60 # Percentage ScaleInCooldown: 90 # Seconds ScaleOutCooldown: 30 # Seconds For other people that are going to analyze the report, it's very important to know what you've load tested against (specs). This gives you the ability to respec your workload later and then test it again, so you can compare reports. |
| Task Count | The number of docker containers that will be launched in the Fargate cluster to run the test scenario, max value 1000. (1000 available). |
| Concurrency | The number of concurrent virtual users generated per task. The recommended limit based on default settings is 200 virtual users. Concurrency is limited by CPU and Memory. Please see the implementation guide for instructions on how to determine the amount of concurrency your test can support. My recommendation is to use 100 concurrency x task. |
| Ramp up | The time to reach target concurrency. If you want to create a realistic approach I would recommend setting a ramp-up time of 15min since we're not stress-testing the application and infra plus the load balancers are probably not pre-warmed so you might get lots of 5xx errors. Here is some more information on creating realistic ramp-up times. |
| Hold for | Time to hold target concurrency. If you plan to do a load test for an hour with a ramp-up time of 15min. Then set this parameter to 45min. |
| Test type | There are two test types available: Single HTTP Endpoint: If you want to check how well a single page performs under load. You can do GET, PUT, POST, and DELETE actions with optional headers and payloads. JMeter: Here you can test a whole workflow with multiple URLs. As an example, you can test a flow that's frequently being done by your users e.g. buy a product and do a checkout. You can choose either a .jmx file or a .zip file. Choose .zip file if you have any files to upload other than a .jmx script file. |
Explanation of the load testing options including sensible defaults and explanation
3.1 Create JMeter script
In most use cases you'd want to test multiple URLs on your target endpoint.
This requires you to make use of Apache JMeter and upload a .jmx file in the "Test type" input field of the "Create test" step.
To easily create your custom JMeter script, you can use this Chrome browser extension tool called: BlazeMeter.
Install the extension, log in, and start recording your activities.
After you're done with recording your HTTP workflow, you can generate a .jmx file that you can use for this load-testing tool.
4. Analyse the load test report
Once your load test has finished, you can check out the details from the dashboard, and click "details".

You'll find more results of the load test, including when it started and ended.

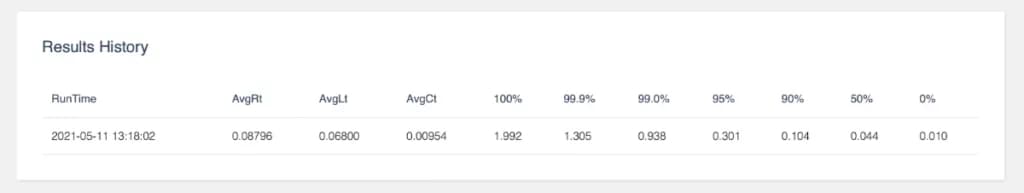
If you scroll down a little further you see the summary of the test result

The summary shows the average response times and latency for all the URLs that we've tested.
In our load test example, we've run a JMeter script that tested multiple URLs, so that means it's also possible to select one URL and see the statistics of those.
If you plan on doing some optimizations on the application and wish to test again under the same circumstances, then you can do so by pressing "start" again from the load test details page.

At the bottom of the same page, you can check the results of the previous load tests that you've done using the same load test configuration.
Conclusion
In this blog post, you learned how you can deploy a distributed load-testing solution from the AWS Solutions library with the use of AWS CloudFormation.
All the steps we're explained in detail to show you how you can set up and pass the required values to run a smooth load test on your target endpoint providing you with useful information on how well your workload handles stress.
If you need help with setting up this solution on your AWS account and need expert advice on how to optimize your application infrastructure to handle more load? Then have a look at this complete solution that I provide as one of my services.
