As you adopt AWS and start growing your business’s needs there comes a point where fitting all your workloads in a single AWS account becomes confusing and harder to manage as time goes by.
Later on, you see the need to add more AWS accounts to make a distinction between your workloads like having separate accounts for Testing, Staging, and Production.
You’ll notice that managing users, security, and compliance becomes harder when you have multiple accounts.
AWS Organizations solves this problem by allowing you to centrally manage and control 100s of AWS accounts efficiently from a single interface.
This guide will explain what AWS Organizations is and how you can set it up yourself using the best practices.
Table of Contents
What is AWS Organizations?
AWS Organizations is an account management service that allows you to centrally manage multiple AWS accounts. It enables you to better meet budgetary, security, and compliance needs as an administrator of an organization.
Some of the features and benefits of using AWS Organizations include:
- Centralized management of all of your AWS accounts
- Consolidated billing for all member accounts within the organization
- Hierarchical grouping of your accounts using Organization Units (OUs) to meet your budgetary, security, or compliance needs
- Policies to centralize control over the AWS services and API actions that each account can access
- Policies to standardize tags across the resources in your organization’s accounts
- Policies to control how AWS artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning services can collect and store data.
- Policies that configure automatic backups for the resources in your organization’s accounts
- Integration and support for AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Running tasks and AWS services on all accounts that are members of the organization
- Its API plays a key role when you’re building a landing zone or a cloud center of excellence as part of your cloud adoption journey.
Sign up for a new AWS account
Before we can begin with enabling AWS Organizations, we need an AWS account first. If you don’t have an AWS account yet, then you can sign up over here in the AWS console
Note: if you already have an AWS account, please proceed with Create an AWS Organization on the management account
Add billing details
Once you’ve created the AWS account you’ll need to add the billing details on the payment methods page of the billing dashboard.
Secure root user
It’s advisable not to use the root user in your AWS account because this user has full privileges to change payment details and delete accounts, etc.
The best practice for doing administrative tasks on an AWS account is to start using IAM users or roles. IAM allows you to easily restrict and control your user’s permissions on the AWS account.
But we can’t just throw away the root user, we need to secure it first using the following steps:
- Enable AWS multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Delete the access keys from the Security credentials page
- Setting up a strong password
Then you can safely store that user in a password manager like 1password for example.
Create an AWS Organization on the management account
To start an AWS Organization, simply head over to AWS Organizations in the AWS console and press Create an organization

Once you’ve created an AWS Organization you’ll see the organization structure in the AWS Organizations > AWS accounts page
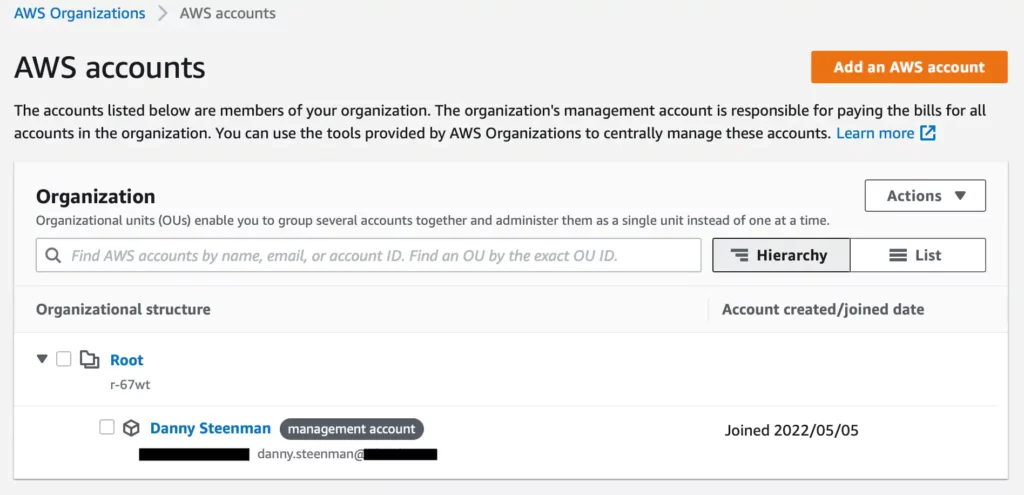
Enable all AWS Organization policies
After creating the AWS Organization you need to enable all the policies in the AWS Organizations > Policies page, so you can make effective use of all its features.
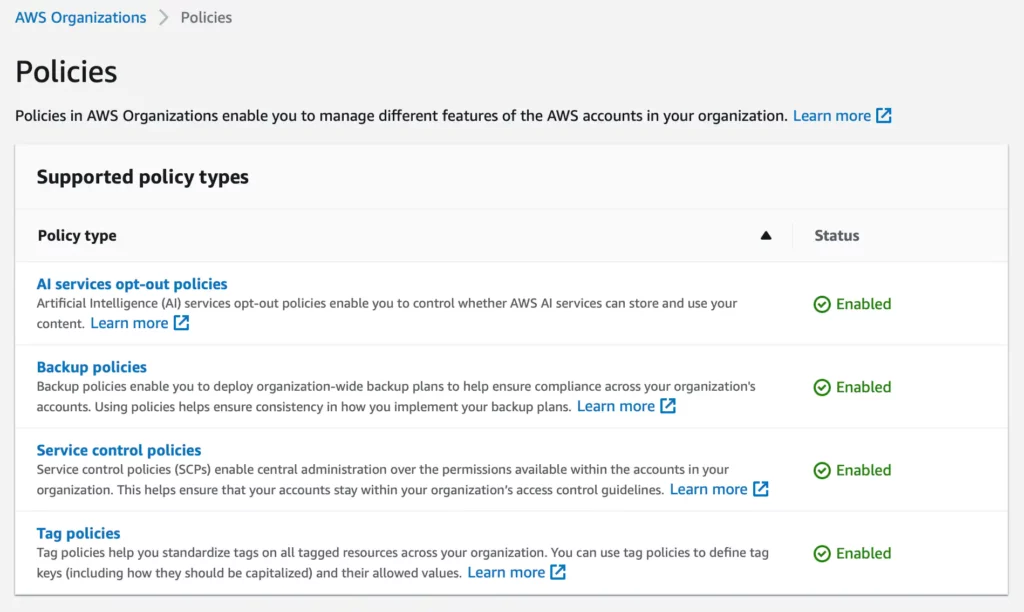
The following policies are available:
- AI services opt-out policies – Artificial Intelligence (AI) services opt-out policies enable you to control whether AWS AI services can store and use your content.
- Backup policies – Backup policies enable you to deploy organization-wide backup plans to help ensure compliance across your organization’s accounts. Using policies helps ensure consistency in how you implement your backup plans.
- Service Control Policies – Service control policies (SCPs) enable central administration over the permissions available within the accounts in your organization. This helps ensure that your accounts stay within your organization’s access control guidelines.
- Tag policies – Tag policies help you standardize tags on all tagged resources across your organization. You can use tag policies to define tag keys (including how they should be capitalized) and their allowed values.
Turn on tax inheritance for AWS billing in your AWS Organization
Tax inheritance allows you to configure tax settings once for the whole organization and consolidate it for all existing and new AWS accounts that join the organization.
This effectively saves you time that you don’t have to spend doing administrative tax tasks when you create a new AWS account.
To enable it, go to the billing dashboard and configure the tax settings first.
As you can see at first, the tax settings haven’t been verified yet.
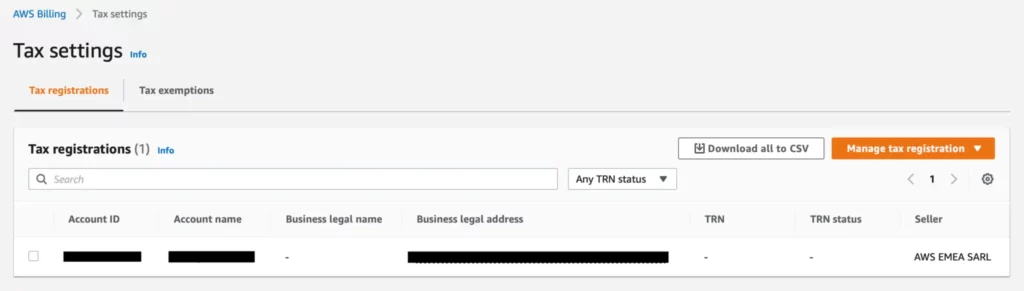
Click on Manage tax registration in the top right corner to configure the customer’s tax settings. Follow the wizard and save the settings.
It takes a couple of minutes for AWS to process and verify your tax registration. Once that succeeded you can proceed and enable the toggle Turn on tax settings inheritance
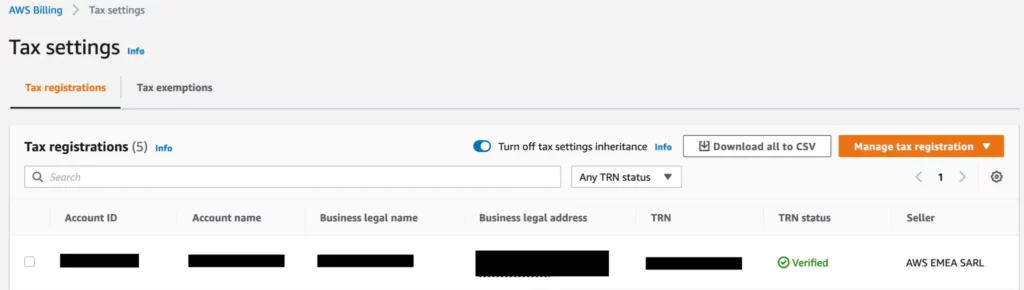
By turning on tax inheritance, it will automatically fill in the tax settings for any new account that you create within an AWS Organization.
Create an AWS account in AWS Organizations
Now that we’ve enabled AWS Organizations and set up the required tax settings we can easily create new AWS accounts in the AWS Organizations dashboard by pressing the Add an AWS account button.

You can proceed and fill in the account name and email address.
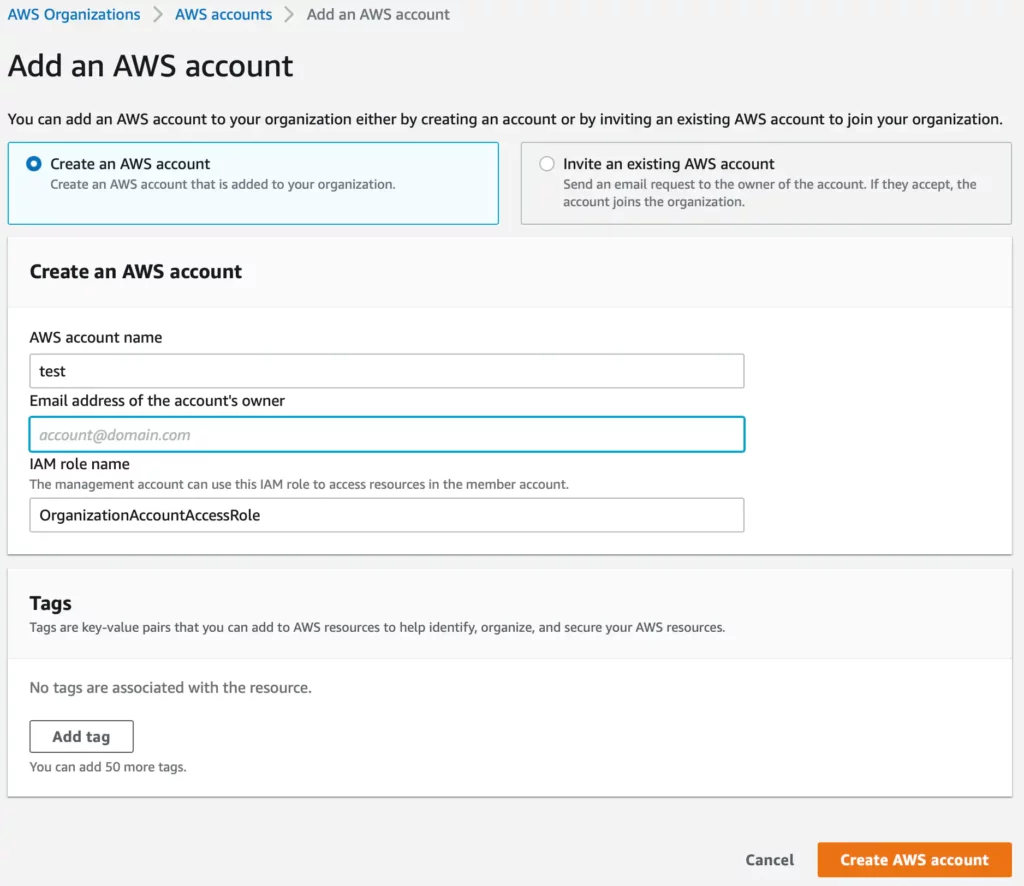
Once you click the Create AWS account button it will proceed and create the account for you and add it to the root of your AWS Organization.

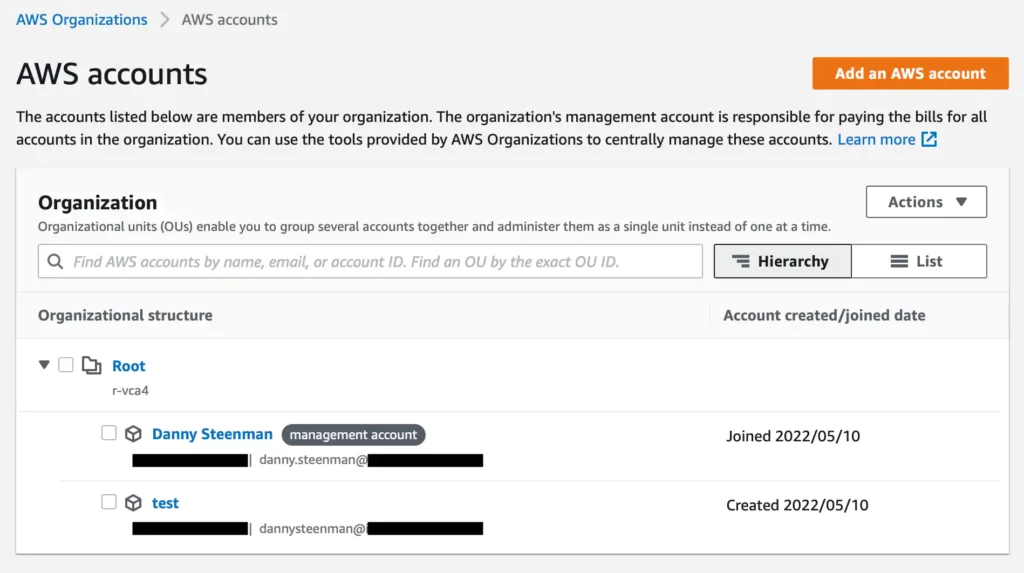
As you can see once, the AWS account is created it will be visible on the AWS Organizations > AWS Accounts page in the AWS Console.
Sign in to the newly created AWS account
In the meantime, you’ll receive an automated email from Amazon stating that the new AWS account is ready.
You can go ahead and activate it by going to the AWS Console sign-in page.
Select sign-in as root using the email of the new AWS account you created and then follow up with the forgot password step.
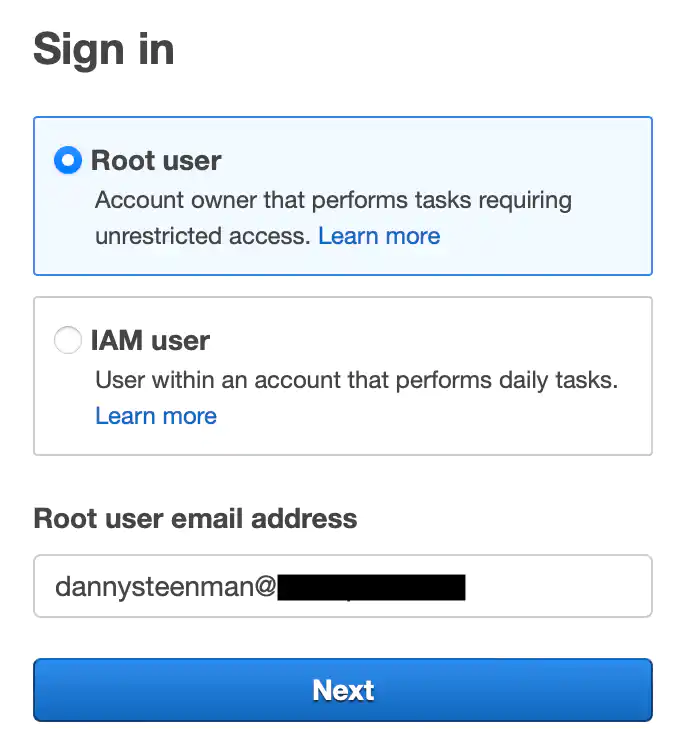
You’ll receive an email with a new password and then you can proceed to sign in.
Once you’re signed in make sure to secure the new root account again by following the instructions as explained in the step Secure root user
Delete an AWS account in AWS Organizations
Deleting an AWS account can be done from the AWS Organizations > AWS accounts page. Click on the account you wish to delete and press close
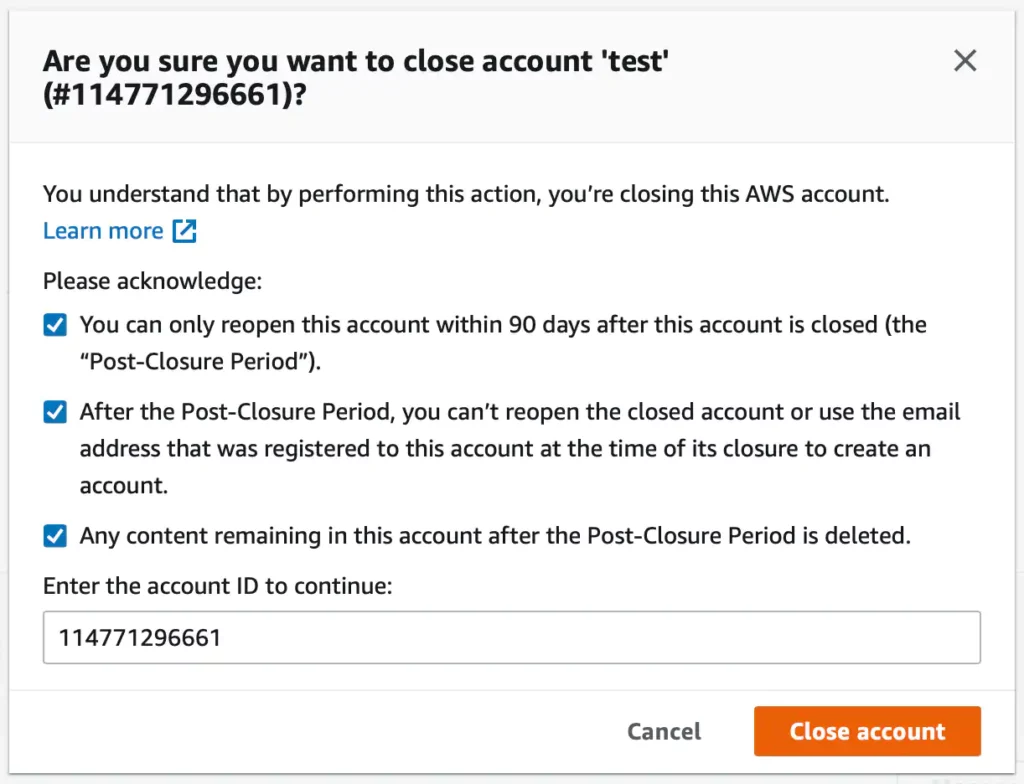
You’ll get a confirmation prompt to validate if you want to close the AWS account permanently. Check the boxes and click Close account
Best practices for organizing AWS accounts in AWS Organizations
Now that you know how you can set up AWS Organizations for your own accounts, it’s time to dive deeper and focus on setting up a correct structure that allows you to control your accounts in a more efficient and effective way.
When you initially create an AWS Organization you start out with the root of that organization that holds all member AWS accounts.
As a best practice, you’ll want to create a hierarchical structure and group similar accounts based on their function using Organizational Units (OUs).
A typical medium size business that manages 10-30 AWS accounts can use an AWS Organization structure like the below:
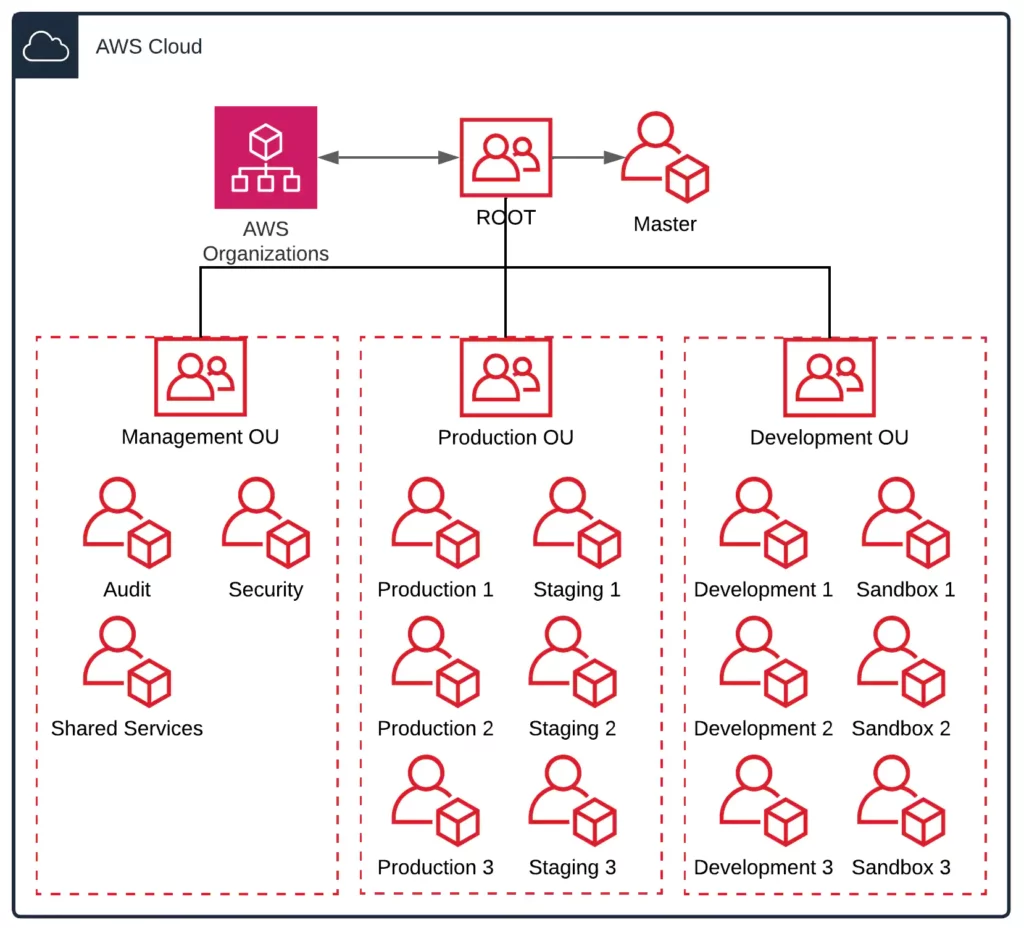
A few key takeaways:
- Avoid nested OUs when possible – You can nest up to 5 levels deep under the root within the organization. Setting up a nested structure can cause confusion on what restrictions apply to certain member accounts that are nested in multiple OUs. For example, if you apply a Service Control Policy on the parent OU, the nested OU automatically inherits all the restrictions that you apply to the parent OU. You can imagine that adding restrictions to multiple layers can add a lot of complexity.
- Keep It Simple, Stupid (KISS) – Use this method to create a single level of OUs like in the example diagram and expand when there is an actual demand for a new OU.
- Organize based on security and operational needs – You’ll need to find a balance between having the freedom to quickly develop and having a stable and secure environment. Therefore it’s a good practice to restrict Production and Staging environments in their own OU as opposed to Development and Sandbox accounts that rely on speed and trying out new services.
- Apply restrictions to OUs instead of accounts – It’s way easier to manage a group of accounts than multiple standalone accounts. So as explained in the previous point, try to organize accounts based on their security and operational needs.
Conclusion
Simply put, AWS Organizations is a great way to consolidate multiple AWS accounts into a single organization that you can easily manage.
It’s a bit complicated to get started at first, but if you plan ahead and followed this guide it can save you loads of time, energy, and money in the long run.
If you followed this guide and you’re looking to add security to your OUs within your AWS Organization.
Then it’s important to start using AWS Service Control Policies (SCPs). I’ve written a complete guide with example SCPS that’ll help you secure and maintain compliance with AWS accounts within the AWS Organization.
AWS Organizations – FAQ
What is the difference between AWS Organizations and AWS Control Tower?
AWS Organizations allow you to centrally manage multiple AWS accounts and apply security guardrails such as Service Control Policies (SCPs).
AWS Control Tower is a landing zone solution AWS offers that contains a full orchestration suite that extends the capabilities of AWS Organizations with other AWS services such as AWS Service Catalog and AWS Single Sign-On.How many accounts can you have in AWS Organizations?
The default maximum number of accounts that can be in an AWS Organization is 10.
However, this is a soft limit of the service quota and it can be increased by contacting AWS Support.What is a master account in AWS Organizations?
The master account in AWS Organizations has full administrative control over how the AWS accounts within the organization are managed.
The billing for the costs is also consolidated on the master account, which means all the costs that are incurred on the member accounts are aggregated and presented to the master account as a single bill.What are the benefits of using AWS Organizations?
The main benefits are getting the ability to control and manage multiple AWS accounts from one central place.
This means you can secure accounts using Security Control Policies (SCPs), centrally manage user access to different accounts and manage tax and payments settings using the consolidated billing feature.



